Overview
Proxies are commonly found on business networks, but they are increasingly becoming popular for personal use. The following tutorial will show you multiple ways of setting your proxy in Ubuntu 18.04, allowing you to browse the Internet with additional privacy.
This tutorial will cover the following three areas. Use the one the fits your needs.
Desktop: learn how to set your proxy settings from within the desktop.
Terminal: set environment variables for your proxy server when using a terminal or console.
All users: setting the proxy settings for all users on the system.
Ubuntu Desktop Network Settings
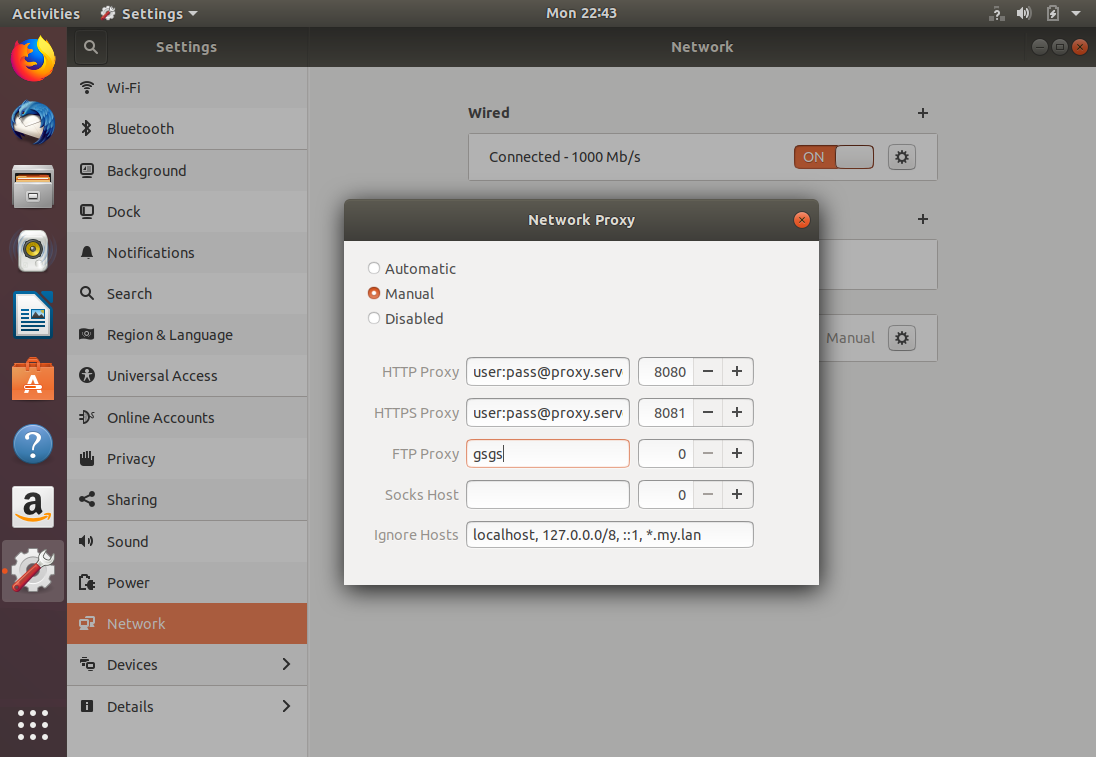
To configure your proxy settings in Ubuntu Desktop you need to access Network Settings. Within there you can set a number of parameters, including proxy settings for HTTP traffic, HTTPS traffic, and FTP traffic.
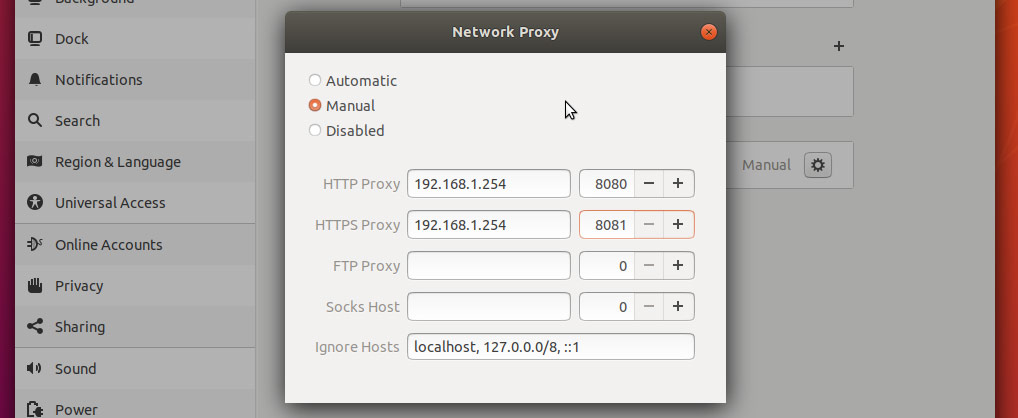
Equally as important as setting your Internet proxy settings is setting Ignore Hosts, to prevent local traffic from going through your proxy server.
To set your proxy in Ubuntu Desktop, do the following:
- Open the Application launcher by clicking the “Show Applications” icon, located at the bottom of the left-hand quick application access bar.
- Type in ‘Settings’
- Click the ‘Settings’ icon.
- From the left-hand navigation, click the Network tab.
- Click the cog icon near the Network Proxy label.
- A dialog box will appear where you can set your proxy settings.
- In the appropriate text fields, enter your proxy server’s hostname or IP address. Ensure you change the port number to match your proxy server’s, too.
- Close the dialog box. Your settings will be automatically saved.
Ubuntu Terminal Proxy Settings
Like every Linux distribution, proxy settings can be set using environment variables. There are a number of variables available to use, ranging from HTTP traffic to FTP traffic.
Proxy settings can be either persistent by setting them in your profile, or non-persistent by setting them from the shell session.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| http_proxy | Proxy server for HTTP Traffic. |
| https_proxy | Proxy server for HTTPS traffic |
| ftp_proxy | Proxy server for FTP traffic |
| no_proxy | Patterns for IP addresses or domain names that shouldn’t use the proxy |
The value for every proxy setting, except for no_proxy, uses the same template. They all require a hostname, but you may optionally specify a proxy server port and your user credentials if required to do so. For example:
proxy_http=username:password@proxy-host:port
Single User Temporary Proxy Settings
You may not always want to force Internet traffic through a proxy. Sometimes you need to override existing settings, and you can do this safely by setting the proxy environment variables from the command line.
The following will set a proxy for HTTP and HTTPS, while preventing local traffic from going through the proxy. Our example proxy server endpoint is my.proxy.server:8080 for HTTP traffic and my.proxy.server:8081 for HTTPS.
- Open a Terminal window where you need proxy access.
- Set and export the HTTP_PROXY variable.
export HTTP_PROXY=user:[email protected]:8080
- Set and export the HTTPS_PROXY variable.
export HTTPS_PROXY=user:[email protected]:8081
- Set and export the NO_PROXY variable to prevent local traffic from being sent to the proxy.
export NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,*.my.lan.domain
Single User Persistent Proxy Settings
- Open your bash profile file into a text editor.
vi ~/.bash_profile
- Add the following lines, modifying them to match your environment.
export http_proxy=username:[email protected]:8080 export https_proxy=username:[email protected]:8081 exprot no_proxy=localhost, 127.0.0.1, *.my.lan
- Save your settings.
- The proxy settings will be applied the next time you start a session, by logging into the server or opening a new Terminal window from a Desktop.
- To force apply your new proxy settings in the current Terminal session, execute the source command against your bash profile.
source ~/.bash_profile
All Users
You will need administrative rights to perform this task. All versions of Ubuntu and Debian have a file called /etc/environment. Within this file, we can set global variables and other such things.
Similar to how you set proxy settings for your own local proxy, we’ll be adding the environment variables to this file. The variables will be set when a new user session is created, which is to say when you log in next.
- Using an administrator account, open /etc/environment into a text editor.
sudo vi /etc/environment
- Add the following lines, modifying them to fit your environment. Username and password may be omitted, if not required.
http_proxy="http://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port>/" https_proxy="http://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port>/" ftp_proxy="http://<username>:<password>@<hostname>:<port>/" no_proxy="<pattern>,<pattern>,...
For example, if you do not need to enter a username or password, and your proxy server is my.proxyserver.net at port 8080, and you do not want local traffic going through the proxy, you would enter the following:
http_proxy="http://my.proxyserver.net:8080/" https_proxy="http://my.proxyserver.net:8080/" ftp_proxy="http://my.proxyserver.net:8080/" no_proxy="localhost,127.0.0.1,::1
- Save your changes and exit the text editor.